In the rapidly changing digital innovation environment, blockchain technology must have definitely been one of the most disruptive ideas to capture industries worldwide. Such a decentralized, secure, transparent ledger system would be bound to alter the way we do transactions, data management, and trust-building across many sectors.
Going down to the inner sanctum of the blockchain, it becomes evident that such disruptive technology has huge potential for reshaping the future course of business and governance and even our daily lives.
Demystification of Blockchain Concept
Blockchain: A decentralized, digital ledger that keeps a record of transactions securely and transparently through cryptography and peer-to-peer networks

A blockchain is actually a digitally kept ledger that comprises an ever-growing list of records segregated into blocks. These blocks, through advanced cryptography, are irrevocably linked to each other to form an unbreakable chain. Each block holds a certain set of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash that links it to the prior block. This means that, once recorded on the blockchain, data is immutable—incapable of being altered or tampered with—and hence provides an unprecedented level of transparency and integrity.
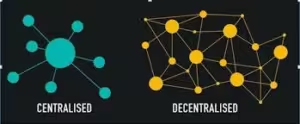
Probably, however, the most important property of blockchain is its decentralized nature. A network in which every node embraces a copy of the entire ledger does not need a central authority. Such character of this model avoids the problem of single-point failure. Along with this, decentralization brings enormous resilience, censorship resistance, and immunity to the manipulation of any single entity.
Initial Principles behind Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralisation:
By copying the ledger on every node in a network, blockchains democratize the system and dispel the central authority or intermediary, thereby becoming more transparent.
2. Transparency:
Every activity is visible to all the parties on the blockchain. In other words, during the process, there exists complete transparency and absolutely no scope for any action to occur without accountability.
3. Immutability:
The cryptographic hashing mechanism itself in blockchain technology gives assurance that, once it is recorded on the ledger, the data cannot be changed or tampered with, hence providing an immutable record of the different transactions.
4. Security:
Blockchain makes use of the newest cryptography and agreed mechanism that secures data to its integrity and security kept on the ledger, hence making it nearly impossible to hack or compromise.
5. Trustless:
This is a digital, decentralized ledger with no central authority or intermediary for transactions; instead, every transaction taking place over the network is checked and verified through the mechanism of reaching the same consensus for the respective transaction.
Real-World Examples: How Blockchain Really Can Make a Difference
1. Financial and Cryptocurrency Applications:
This is the technology backing digital cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. It facilitates secure, transparent financial transactions without using an intermediary bank. This thus gives likely features or reduces transaction costs, rises in efficiency, and increases reach toward financial inclusion of unbanked people. To put it differently, removing the middlemen will bring down transaction costs.

2. Supply Chain Management:
The blockchain, being immutable and transparent, is an ideal solution for supply chain management. This can be achieved through the recording by blockchain of every step in a product’s journey, right from the raw materials to the finished goods. It thereby gives a trail that is individually audit-worthy and thus improves transparency, traceability, and accountability in the whole supply chain process.
3. Blockchain in Healthcare:
This much speaks to why being decentralized, blockchain has enormous potential benefits for the health sector. High-level encryption within a blockchain will ensure the sharing of medical records among healthcare providers safely, thus improving coordination, and maintaining integrity, all while protecting the privacy of the patient. This can further be useful in areas of drug supply chain management, data sharing generated during clinical trials and health insurance claim processing.
4. Identity Management:
Identity management in both secure and decentralized forms is essential in today’s digital world. Blockchain can provide a way for tamper-proof and reliable methods of handling digital identity management, which eventually solves problems relating to identity theft and fraud. This retains identity data stored on the blockchain, keeping these persons in control of their data and at liberty to share it with entities at their own will.

5. Governance:
It can further drive transparency and accountability into governance with systems of secure, transparent voting, public keeping of records, and execution of smart contracts. The use of blockchain for its immutability and decentralization will therefore ensure increased public trust in institutions, hence achieving greater citizen engagement.
6. Intellectual Property Rights:
Further areas in which blockchain technology can be applied include its use in the protection and management of intellectual property rights in the music, art, and publishing industries. Considering only this technology, which ensures that a creator’s IP can never be utilized without consent, through recorded ownership and usage rights, creators could trace and monetize their works with self-sovereign identity.
7. Internet-of-Things (IoT)
This technology can bring a lot to secure, decentralized communication between devices as the number continues to grow. Blockchain then realizes a condition where any central authority is eliminated and facilitates trustless data exchange. It means that automation of transactions shall give way to new possibilities concerning smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation. Curious about how this is possible? Check our in-depth article on the Internet of Things(IoT).
Up Next, Blockchain Future: Challenges and Opportunities.
Notwithstanding, this huge potential technology has problems of its own. There are huge scalability challenges. With increasing transactions in blockchain networks, so is the bottleneck for processing speed and efficiency. Since this is a problem being handled, several solutions are currently being researched to see its way out; these involve sharding, off-chain transactions, and side chains so that blockchain eventually handles large applications.

The second presents a problem of coming up with regulatory frameworks and industry standards. On that note, with the ever-growing preeminence of blockchain technology, governments and regulators will have to think through the gravity of having in place an enabling environment set up with clear guidelines and policies on this technology so that its application is responsible and serves the best interest of all stakeholders.
In sharp contrast to decentralization, immutability, and transparency—core tenets of this tech—should be base builders for a future much more secure, efficient, and trustless. With this technology maturing and further seeing extensive adoption, it would lead to a number of innovative application trees across different industries, thereby driving digital transformations that reshape how one can engage, transact, and exchange value with one another.
Unlocking the Future: The Power of Blockchain Technology
This technological revolution is anything but a technological shift. Looks like a tectonic change in the paradigm about how we view and administer matters of trust, transparency, and accountability. With all stakeholders, starting from individuals to businesses to governments, adjusting them to this disruption brought about by technology, embracing it and harnessing its power becomes the sine qua non.
This, therefore, allows businesses to smoothen their operations, reduce expenses, and increase customers’ trust. Enhanced transparency and supply chain management can be offered to companies by integrating blockchain solutions. Moreover, this provides an opportunity to form a more secure and reliable ecosystem for one’s ops.

Governments could exploit such technology to better public services, democratic procedures, and interactions with citizens. If blockchain-based solutions are adopted for e-voting systems, public record-keeping, or the execution of smart contracts, this would greatly bring about transparency, accountability, and general trust in public institutions.
People can further accelerate this technology as both consumers and citizens. Consider the fact that support and participation in blockchain-based platforms and applications are already a vote for an empowered decentralized, more transparent, and secure digital future.
To learn more about Blockchain, read our posts on;
Best 3d Printer for Beginners: A Beginner’s Guide to the Best Machines
Robotics: Our Mechanical Companions in the Journey to the Future
Neuroscience Unveiled: Your Brain’s Universe Explored
5G and Beyond: Revolutionizing Wireless Communication
Biotechnology: Harnessing Nature’s Toolbox
Case Studies and Professional Insights:
Case Study 1: Financial and Cryptocurrency Applications
This technology has made transactions in finance extremely disrupted with the rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Digital currencies are mostly characterized by blockchain decentralized networks that do not have any middleman, like banks. One example is Bitcoin, which fulfils peer-to-peer transactions across the globe, hence making it much cheaper and increasing the speed of transactions compared to traditional banking systems. Such disruption received global attention and resulted in innovation in DeFi and asset tokenization.

Professional Insight 1:
This is the transparency and immutability brought to the supply chain management process by blockchain, according to a Deloitte report. For instance, Walmart deploys blockchain to trace the farm-to-store journey of mangoes. It allows for the quality of mangoes to be traced, and in case the quality is not found to be good, trace food wastage effectively. That transparency only helps enhance consumer trust and operational efficiency across the supply chain.
Case Study 2: Blockchain in Healthcare
This technology enhances the security of patient data, improving and smoothening health operations in the country. Blockchain-based digital identities, for example, have been used in Estonia to provide secure access for citizens and share their medical records with doctors and health care centres, improving privacy for patients and coordination in health care. Innovations like these demonstrate blockchain’s dexterity at enhancing the integrity and interoperability of health information systems worldwide.
Professional Insight 2:
Digital identity, in its entirety, is secured and tamper-proof with IBM’s blockchain for identity management. This technology allows every individual to be in control of their personal data, reducing all possible risks of identity theft or fraud. Governments and enterprises can use blockchain to enhance data security and compliance in accordance with regulatory standards. Blockchain can establish trust in every kind of digital interaction.
Case Study 3: Blockchain in Governance
It enhances transparency and accountability in governance. In the Republic of Georgia, blockchain is used for land registry, a corruption-reducing means that makes sure satisfaction in property rights is guaranteed. Smart contracts allow effective and safe property transactions, enhancing trust by citizens in public institutions and boosting the economy due to reliable property records.

Professional Insight 3:
The United Nations comments that it provides secure and transparent voting systems. Blockchain-based voting platforms ensure verifiable election results and reduce risks of electoral fraud. This technology encourages democratic processes around the globe, hence allowing citizens to trust in electoral integrity and be assured by government accountability.
Conclusion
As navigation through this exciting journey of blockchain adoption is done, it’s very critical to appreciate its transformative power while solving complex problems lying ahead. Only through building collaboration among stakeholders, developing robust regulatory frameworks. Investing in research and development can the potential concealed within this groundbreaking technology. Be truly unlocked and pave an effective path toward a future that’s secure, efficient, and trustless.
References:
1. “Blockchain Technology: Opportunities and Challenges” by ResearchGate (https://www.researchgate.net/publication/378313906_Blockchain_Technology_Opportunities_and_Challenges)
2. “The Truth About Blockchain” by Harvard Business Review (https://hbr.org/2017/01/the-truth-about-blockchain)
3. “Blockchain and the Future of Supply Chain Management” by Deloitte (https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/operations/articles/blockchain-supply-chain-innovation.html)
4. “Blockchain in Healthcare: A Primer” by MIT Technology Review (https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/12/23/131844/blockchain-in-healthcare/)
5. “Blockchain and Governance” by the United Nations (https://www.un.org/en/blockchain-for-digital-governance/)


